Symptoms and causes
A congenital thoracic malformation like Pectus or Poland alters the anatomy of the anterior thoracic base and affects the appearance, position and orientation of the breasts.
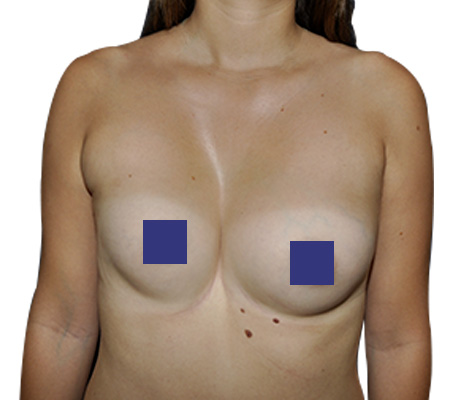
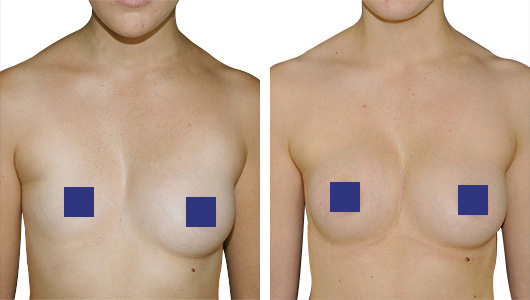
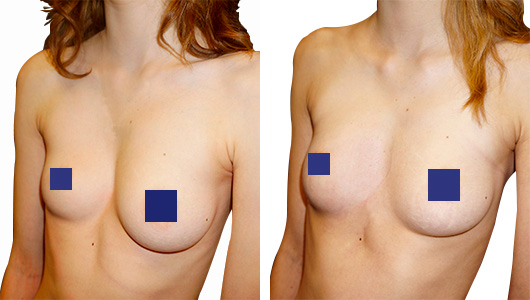
Pectus Excavatum can be at the origin of women breast defects : Convergence, divergence, asymmetry. Poland Syndrome is also frequently associated with asymmetry, sometimes with a phenomenon of tuberous breasts.
Treatment of breast asymmetry
The first step is always to correct the thoracic malformation. This allows reconstruction, through the breast base, of an anatomically normal and symmetrical profile. Breast implants are not a first-line solution: the thoracic deformity must be corrected first of all.
A 2-phase procedure is required: firstly involving the custom-made thoracic implant, followed 6 months later (on average) by the placement of breast implants, if required.
Thoracic correction may be sometimes all that is needed for the restructuring of the chest.
If there is insufficient mammary volume in the breasts (breast hypotrophy), a secondary breast enlargement will be performed using one or two silicone gel implants, in a different plane to the thoracic implant.
If the breast implants are already in place at the time of the operation, particularly in a retromuscular position, (Pectus), it is recommended that they are removed and the customised 3-D thoracic implants are placed in the retromuscular position. This avoids displacement of the breast implants, one against the other, and the appearance of an unattractive «synmastia».
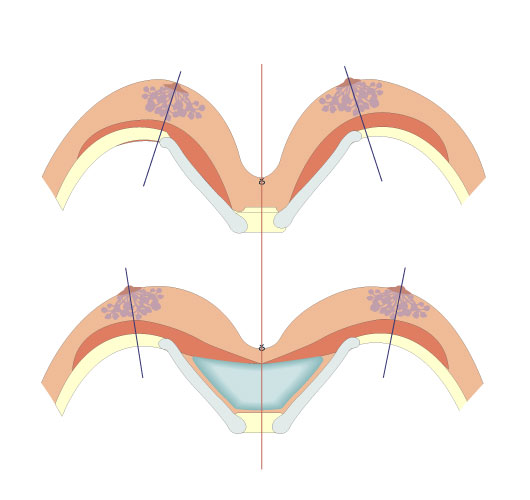
Pectus type 1 - slight convergence
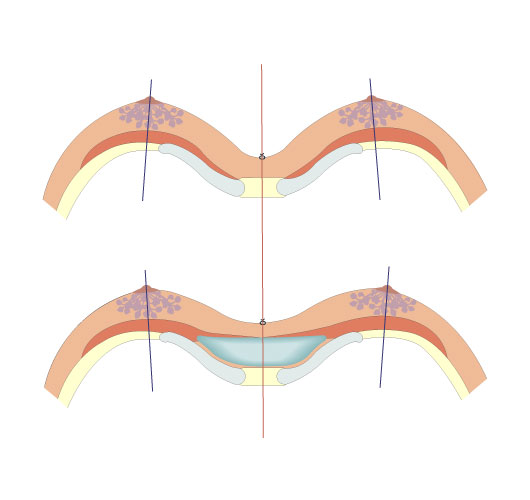
Pectus type 2 - strong convergence
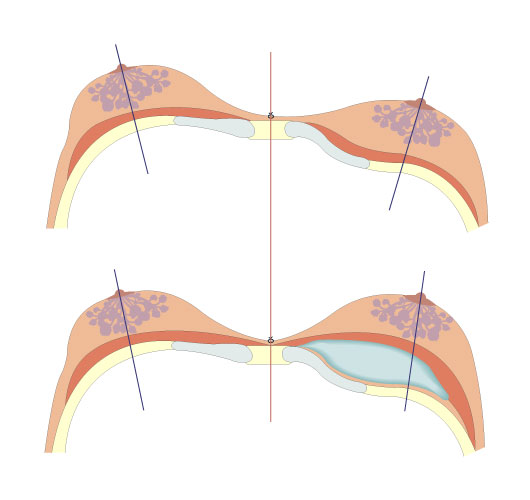
Pectus type 3 - asymmetry